图片来自官方文档。
bindService方式启动的入口在ContextImpl,这里假设是在独立的进程里面启动,对应的时序图。
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, Process.myUserHandle());
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
//...
//mPackageInfo为LoadedApk
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
//将ServiceConnection与ServiceDispatcher关联起来
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
validateServiceIntent(service);//验证Intent
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
//...
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(),
service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, user.getIdentifier());
//...
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return false;
}
}
mPackageInfo是LoadedApk类型,调用getServiceDispatcher将ServiceConnection与ServiceDispatcher关联,并存储在mServices容器里面:
//每个进程维护一个LoadedApk实例,Context有多个实例(比如多个Activity)
public final class LoadedApk {
private final ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>> mServices
= new ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>>();
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
}
ServiceDispatcher内部保存了InnerConnection和ServiceConnection对象,用于当服务绑定,调用ServiceConnection#onServiceConnected:
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
//使用WeakReference防止客户端退出AMS还持有InnerConnection引用以至内存泄漏
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
先分析客户端发起请求的过程,ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()得到ActivityManagerProxy,调用bindService:
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
进入到ActivityManagerService执行bindService:
final ActiveServices mServices;
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType,
IServiceConnection connection, int flags, int userId) {
//...
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service, resolvedType,
connection, flags, userId);
}
}
调用ActiveServices#bindServiceLocked进行下一步处理:
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType,
IServiceConnection connection, int flags, int userId) {
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
ActivityRecord activity = null;
//如果是在Activity里执行的绑定操作,则token不为空
if (token != null) {
//Activity是否在栈中
activity = ActivityRecord.isInStackLocked(token);
if (activity == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Binding with unknown activity: " + token);
return 0;
}
}
int clientLabel = 0;
PendingIntent clientIntent = null;
//...
final boolean callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != Process.THREAD_GROUP_BG_NONINTERACTIVE;
//使用PackageManagerService解析出Intent里面对应的ServiceRecord
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true, callerFg);
if (res == null) {
return 0;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return -1;
}
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
//从mRestartingServices里面去掉要绑定的ServiceRecord
if (unscheduleServiceRestartLocked(s, callerApp.info.uid, false)) {
//...
}
//将调用进程和被调用进程关联起来,存储在ActivityManagerService#mAssociations
mAm.startAssociationLocked(callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName,
s.appInfo.uid, s.name, s.processName);
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
//表示一个客户端的连接
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
s.connections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
b.connections.add(c);
if (activity != null) {
if (activity.connections == null) {
activity.connections = new HashSet<ConnectionRecord>();
}
activity.connections.add(c);
}
b.client.connections.add(c);
//BIND_ABOVE_CLIENT告诉AMS绑定Service的优先级比客户端要高
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ABOVE_CLIENT) != 0) {
b.client.hasAboveClient = true;
}
if (s.app != null) {
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(s.app, c, true);
}
clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
mServiceConnections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
//Service没有启动则启动Service
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
if (s.app != null) {
//...update process
}
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
//...
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
//...
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return 1;
}
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r,
IntentBindRecord i, boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
// If service is not currently running, can't yet bind.
return false;
}
//...
}
如果是在Activity里执行的绑定操作,验证一下Activity是否在栈中。然后将调用进程和被调用进程关联起来,存储在ActivityManagerService#mAssociations。AppBindRecord表示为一个ServiceRecord和他所有客户端的连接,ConnectionRecord表示一个客户端连接。
如果我们调用bindService的第三个参数设置了Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE则会在Service没有启动的情况下启动Service。所以就会执行bringUpServiceLocked来启动Service。
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
int intentFlags, boolean execInFg, boolean whileRestarting) {
//Service已启动,直接调用sendServiceArgsLocked,注意这里客户端不会调用onStartCommand。
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
//...一些延迟启动的处理
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
final String procName = r.processName;
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
//...
} else {
//...
app = r.isolatedProc;
}
if (app == null) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
//...
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
//...
//将ServiceRecord加入mPendingServices里,等进程启动后做处理
if (!mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
mPendingServices.add(r);
}
return null;
}
接着就会调用ActivityManagerService#startProcessLocked开启新的进程,并将当前的ServiceRecord加入mPendingServices里,等进程启动后做处理。
前面bindServiceLocked方法里,由于Service的进程没有启动,所以就不会执行后面的操作。
开启新的进程入口就是ActivityThread#main:
public final class ActivityThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
//...
if (!system) {
//...
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
//...
}
}
}
新进程启动后就会调用,ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()得到ActivityManagerProxy,向ActivityManagerService发起IPC调用(同步),所以就进入到了ActivityManagerService#attachApplication:
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
ProcessRecord app;
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
final String processName = app.processName;
//...
app.makeActive(thread, mProcessStats);
app.curAdj = app.setAdj = -100;
app.curSchedGroup = app.setSchedGroup = Process.THREAD_GROUP_DEFAULT;
app.forcingToForeground = null;
updateProcessForegroundLocked(app, false, false);
app.hasShownUi = false;
app.cached = false;
app.killedByAm = false;
//...
try {
//...
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass,
profilerInfo, app.instrumentationArguments, app.instrumentationWatcher,
app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode, enableOpenGlTrace,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked());
updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
app.lastRequestedGc = app.lastLowMemory = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
//...
boolean badApp = false;
// Find any services that should be running in this process...
if (!badApp) {
try {
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown starting services in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
//...
return true;
}
首先会调用客户端的ApplicationThread#bindApplication,让客户端做一些初始化工作。
然后让ActiveServices执行attachApplicationLocked处理刚才放入到mPendingServices里面的ServiceRecord里面。
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord proc, String processName)
throws RemoteException {
boolean didSomething = false;
if (mPendingServices.size() > 0) {
ServiceRecord sr = null;
try {
for (int i=0; i<mPendingServices.size(); i++) {
sr = mPendingServices.get(i);
if (proc != sr.isolatedProc && (proc.uid != sr.appInfo.uid
|| !processName.equals(sr.processName))) {
continue;
}
mPendingServices.remove(i);
i--;
proc.addPackage(sr.appInfo.packageName, sr.appInfo.versionCode,
mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(sr, proc, sr.createdFromFg);
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//...
}
}
//...
return didSomething;
}
找到要处理的ServiceRecord调用realStartServiceLocked做进一步处理:
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
//...
r.app = app;
r.restartTime = r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
app.services.add(r);
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked();
boolean created = false;
try {
//通知创建Service并执行onCreate
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
//...
} finally {
//...
}
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(app, null, true);
//这里不会加入到pendingStarts里面,所以不会执行onStartCommand
if (r.startRequested && r.callStart && r.pendingStarts.size() == 0) {
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
null, null));
}
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
//...
}
IPC调用客户的ApplicationThread#scheduleCreateService(异步), 通知创建Service并执行onCreate。然后调用requestServiceBindingsLocked做绑定服务的下一步处理,这里创建的Service并不会回调onStartCommand方法:
private final void requestServiceBindingsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg) {
//找到特定Intent启动的请求实例
for (int i=r.bindings.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
IntentBindRecord ibr = r.bindings.valueAt(i);
if (!requestServiceBindingLocked(r, ibr, execInFg, false)) {
break;
}
}
}
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r,
IntentBindRecord i, boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
// If service is not currently running, can't yet bind.
return false;
}
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG, "Crashed while binding " + r);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
调用requestServiceBindingLocked做进一步处理,通过ApplicationThread执行scheduleBindService进入到ActivityThread里面的handleBindService,然后修改IntentBindRecord里面的状态。
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
/...
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
//...
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
}
}
这里就会找到对应的Service,然后调用onBind得到返回的Binder对象,把其传递给ActivityManagerService做处理,就进入到ActivityManagerService里的publishService:
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
//...
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
进一步交给ActiveServices处理,执行publishServiceLocked:
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
//...
continue;
}
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
从Service的connections找到刚才存入的ConnectionRecord,然后向绑定服务的客户端发起IPC调用,执行c.conn.connected,第二个参数就是Service执行onBind返回的Binder对象,所以就进入到前面创建对象InnerConnection的connected方法里面:
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
得到一个ServiceDispatcher对象,继续执行connected方法:
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
mActivityThread是创建的时候关联的主线程Handler对象,不为空,就往主线程里post了一个Runnable对象,在主线程里面执行,所以后面回调接口onServiceDisconnected/onServiceConnected是在主线程里面执行的。
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
final int mCommand;
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command;
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService);
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
}
前面传进来的mCommand为0,所以执行LoadedApk里面的doConnected方法:
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
//...
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
//服务已经绑定了并且返回的Binder与之前的一样就直接返回
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
mDied = false;
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//...
}
} else {
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
如果原来已经绑定过服务则判断原来的Binder和新的Binder是否一样,如果一样就直接返回。
然后就直接回调前面已经注册的ServiceConnection#onServiceDisconnected。

图片来自官方文档。
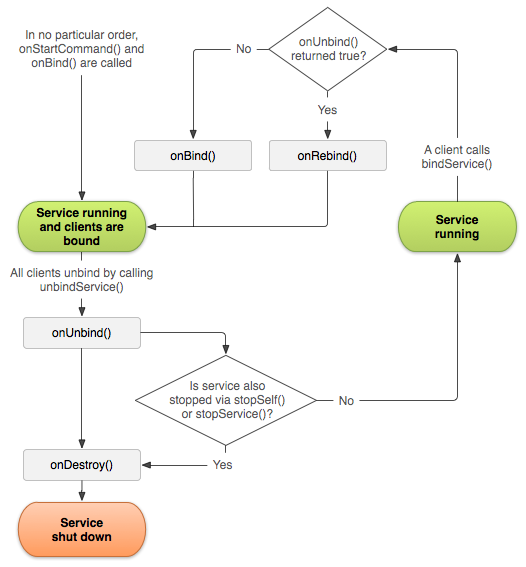
当所有绑定的客户端都解绑的时候,会执行onUnbind,如果Service没有处于started状态(通过startService的方式启动),就会直接onDestroy,如果处于Started状态,Service会处于Running状态,当再有客户端来绑定的时候,如果onUnbind返回true,则会调用onRebind,否则会调用onBind,当然这两种情况,客户端都能正确得到Service published的Binder对象。
unbindService的入口也在ContextImpl里:
final LoadedApk mPackageInfo;
@Override
public void unbindService(ServiceConnection conn) {
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
IServiceConnection sd = mPackageInfo.forgetServiceDispatcher(
getOuterContext(), conn);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().unbindService(sd);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
}
//------------------------------LoadedApk----------------------------------------
private final ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>> mServices
= new ArrayMap<Context, ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>>();
public final IServiceConnection forgetServiceDispatcher(Context context,
ServiceConnection c) {
synchronized (mServices) {
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map
= mServices.get(context);
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
if (sd != null) {
map.remove(c);
sd.doForget();
if (map.size() == 0) {
mServices.remove(context);
}
//...
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
//...
}
}
调用mPackageInfo#forgetServiceDispatcher把客户端绑定时候存储的ServiceConnection移除并返回对应的IServiceConnection对象,利用ActivityManagerProxy向AMS请求unbindService,然后就进入到了ActivityManagerService的unbindService方法中:
public boolean unbindService(IServiceConnection connection) {
synchronized (this) {
return mServices.unbindServiceLocked(connection);
}
}
调用ActiveServices做下一步处理:
final ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>> mServiceConnections
= new ArrayMap<IBinder, ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>>();
boolean unbindServiceLocked(IServiceConnection connection) {
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
return false;
}
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
while (clist.size() > 0) {
ConnectionRecord r = clist.get(0);
removeConnectionLocked(r, null, null);
if (clist.size() > 0 && clist.get(0) == r) {
clist.remove(0);
}
//...
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return true;
}
mServiceConnections存储着客户端所有的连接,通过IServiceConnection找到绑定服务里面存储的ConnectionRecord,调用removeConnectionLocked进一步处理:
void removeConnectionLocked(ConnectionRecord c, ProcessRecord skipApp, ActivityRecord skipAct) {
IBinder binder = c.conn.asBinder();
AppBindRecord b = c.binding;
ServiceRecord s = b.service;
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
if (clist != null) {
clist.remove(c);
if (clist.size() == 0) {
s.connections.remove(binder);
}
}
b.connections.remove(c);
if (c.activity != null && c.activity != skipAct) {
if (c.activity.connections != null) {
c.activity.connections.remove(c);
}
}
if (b.client != skipApp) {
b.client.connections.remove(c);
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ABOVE_CLIENT) != 0) {
b.client.updateHasAboveClientLocked();
}
if (s.app != null) {
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(s.app, c, true);
}
}
clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist != null) {
clist.remove(c);
if (clist.size() == 0) {
mServiceConnections.remove(binder);
}
}
mAm.stopAssociationLocked(b.client.uid, b.client.processName, s.appInfo.uid, s.name);
if (b.connections.size() == 0) {
b.intent.apps.remove(b.client);
}
if (!c.serviceDead) {
//所有的绑定的客户端都解绑了
if (s.app != null && s.app.thread != null && b.intent.apps.size() == 0&& b.intent.hasBound) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(s, false, "unbind");
/...
b.intent.hasBound = false;
b.intent.doRebind = false;
s.app.thread.scheduleUnbindService(s, b.intent.intent.getIntent());
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
}
//如果bindService的flag有BIND_AUTO_CREATE的标志位,bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked里会判断是否还
//有其他连接然后销毁Service。
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
boolean hasAutoCreate = s.hasAutoCreateConnections();
//...
bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked(s, true, hasAutoCreate);
}
}
}
清理AMS存储的ConnectionBindRecord。当所有绑定的客户端都解绑了就会调用客户端的ApplicationThread#scheduleUnbindService(异步),进入到了ActivityThread里执行handleUnbindService。接着就执行bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked,做Service的销毁工作。先看scheduleUnbindService:
ActivityThread:
private void handleUnbindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
boolean doRebind = s.onUnbind(data.intent);
try {
if (doRebind) {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().unbindFinished(
data.token, data.intent, doRebind);
} else {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
}
}
找到Service实例然后执行onUnbind方法,默认返回false,就会执行ActivityManagerProxy#serviceDoneExecuting,进入到AMS的serviceDoneExecuting:
public void serviceDoneExecuting(IBinder token, int type, int startId, int res) {
synchronized(this) {
//...
mServices.serviceDoneExecutingLocked((ServiceRecord)token, type, startId, res);
}
}
调用ActiveServices#serviceDoneExecutingLocked做处理:
void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, int type, int startId, int res) {
boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);//false
if (r != null) {
if (type == ActivityThread.SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_START) {
//...
} else if (type == ActivityThread.SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_STOP) {
if (!inDestroying) {
//...
} else if (r.executeNesting != 1) {
//...
r.executeNesting = 1;
}
}
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
} else {
//...
}
}
private void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean inDestroying,
boolean finishing) {
r.executeNesting--;
if (r.executeNesting <= 0) {
if (r.app != null) {
r.app.execServicesFg = false;
r.app.executingServices.remove(r);
if (r.app.executingServices.size() == 0) {
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r.app);
} else if (r.executeFg) {
for (int i=r.app.executingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
if (r.app.executingServices.valueAt(i).executeFg) {
r.app.execServicesFg = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (inDestroying) {
mDestroyingServices.remove(r);
r.bindings.clear();
}
}
r.executeFg = false;
//...
if (finishing) {
if (r.app != null && !r.app.persistent) {
r.app.services.remove(r);
}
r.app = null;
}
}
}
状态的清除工作。
再回到bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked里,判断销毁服务的条件(所有客户端解绑并且没有处于Started状态)是否满足,并且不能在即将启动发Service里面,不满足就直接返回。
private final void bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn,
boolean hasConn) {
if (isServiceNeeded(r, knowConn, hasConn)) {
return;
}
if (mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
return;
}
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
}
private final void bringDownServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r) {
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> c = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<c.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord cr = c.get(i);
cr.serviceDead = true;
try {
cr.conn.connected(r.name, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
}
}
//...
if (r.app != null) {
r.app.services.remove(r);
if (r.app.thread != null) {
updateServiceForegroundLocked(r.app, false);
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, false, "destroy");
mDestroyingServices.add(r);
r.destroying = true;
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(r.app);
r.app.thread.scheduleStopService(r);
} catch (Exception e) {
//...
}
} else {
//...
}
} else {
//...
}
//...
}
回调InnerConnection的connected方法:
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
这个就和上面回调类似了,由于这个的Binder传递进来的为空,所以就会回调onServiceDisconnected方法。然后有通过Binder调用ApplicationThread的scheduleStopService方法,客户端找到对应Service实例,回调onDestroy方法。